1. Explain why continual quality improvement is important?
The reason why continual quality improvement is important is that it is fundamental to success in the global marketplace. The concept applies to processes and the people who operate them as well as to the products resulting from the processes. And all three- processes, people, and products – must be continually improved. That is why it is so important. A company that is just maintaining the status to quo in such key areas as new product development, adoption of new technologies, and process performance is like a runner who is standing still in a race. Athletes who don’t improve continually are not likely to remain long in the winner’s circle. The same is true of companies that must compete globally. Customer needs are no t static; they change continually. A special product feature that is considered innovative today will be considered just routine tomorrow. The only way a company can hope to compete in the modern marketplace is to improve continually.
2. What is management’s role in continual quality improvement ?
Managers are leaders, and must lead in “total quality”. The managers would have to establish a Quality Control department, and to work with the department closely. Corporate Quality policies with continuous improvement goals must be established and followed. Managers must be supportive of the department with resources, such as measurement instruments, educational materials, office supplies, capital, and affirmation. Managers must schedule audits, inspections, and giving compliments to encourage good practice.
3. Discuss the Kaizen approach.
Kaizen approach in the name given by the Japanese to the concept of continual incremental improvement which means making changes for the better on a continual, never-ending basis. The improvement aspect of Kaizen refers to people, processes and products.
The underlying value system of Kaizen can be summarized as continual improvement of all things, at all levels, all the time, forever. All of the strategies for achieving this fall under the Kaizen umbrella. Executive managers, middle managers, supervisors, and line employees all play key roles in implementing Kaizen.
If management praises someone for a quality change resulting in improvement in product or service, it will most likely encourage others to be open to change. Some of the areas that management must consider for Kaizen are customer focus, teamwork, quality circles, employee/management relationships, and automation.
4. How would you describe a lean system?
A lean system focuses on doing more with less. It emphasizes adding more effort in conduct activities that add value to a finish product or service, while reducing activities that does not add value to the finish product or service over a long term. It is about being flexible enough to get the rights things, to the right place, at the right time, in the right amounts. At the heart of the concept are the reduction of waste and the improvement of work flow.
5. What is lean six-sigma and how would you apply it to a quality management system?
Six Sigma is a broader concept of Total Quality with a goal to achieve a defect rate of 3.4 per million or less. By attaining this goal will make a company in the service and manufacturing industries more competitive. The Six Sigma here is the full-bodied, potent improvement system and the lean part is the complete and proven Quality Management system found in the Toyota Production System and Just-In-Time. The two complement each other with their strengths, namely Lean’s elimination of waste and Six Sigma’s breakthrough methodology for solving performance problems and making improvements. Through the process of identifying the needs of customers, classifying the needs of customers by rank, and determine the process variation for each customer need, and addressing all critical areas that need improvement, the companies will benefit in the areas of cost reduction, productivity improvement, and cycle time reduction.
6. Define benchmarking. Define Auditing. How does benchmarking and auditing relate to each other?
Benchmarking is the process of comparing companies’ processes against the best of its class in a given industry. It is also the process to determine the secrets of success of any function, in order to close the gap with a company that is the best of its class. Whereas, Auditing is the on-site verification activity, such as inspection or examination, of a process or quality system, to ensure compliance to requirements. An audit can apply to an entire organization or might be specific to a function, process, or production step.
From the definitions, auditing and benchmarking go side by side. While benchmarking ensures that a product or service provided is comparable to the best in class, auditing ensures that this quality of product is maintained across the production line.
7. How can you apply benchmarking data in auditing processes, systems, designs, products, factories and services?
The benchmarking data we collected must be analysed thoroughly in comparison with the data taken from its own process. After the team concludes that there is no doubt that the partner’s process is superior, they should try to answer the following questions:
- Can its process replace ours?
- What will it cost?
- Can we afford it?
- What impact will it have on adjacent processes?
- Can we support it?
The quantitative information is effectively the “stake driven into the ground” as the point from which future progress is measured. Qualitative information covers such matters as personnel, policies, training, management styles and hierarchy, total quality maturity and so on.
The quantitative data are clearly the information sought and are always used. However, there may be more value in the qualitative information. It describes the atmosphere and environment in which best-in-class can be developed and sustained. Do not ignore it. Take it very seriously. Study it, discuss it in staff meetings, and explore the possibilities of introducing these changes into your culture.
8. What is a JIT system?
Just-In-Time (JIT) system is the system making products only when needed from materials that were made available by suppliers only as required. It is developed from Toyota Production System. JIT manufacturers let their suppliers keep their materials inventory until the manufacturers need it. JIT permits the production of only what is needed, only when it is needed, and only in the quantity needed.
9. What are the benefits of JIT/lean?
There are numerous benefits of the JIT/Lean system enjoyed by companies. The benefits are based on four main areas, which are :
Inventory and Work-In-Process: JIT/Lean attempts to drive inventory to zero. But in real world, zero inventory makes no sense. The real objective is to minimize the inventory to the maximum possible extent without shutting down production. The company-minimizing inventory will reduce cost of production, and continual improvement will become a reality, which results in more savings.
Cycle Time: Production cycle time is defined as the period bounded by the time materials are sent to the manufacturing floor for the making of a product and the time the finished goods are dispatched from the manufacturing floor to a customer or to finished goods storage. When the cycle time is lowered, production cost is lowered.
Continual Improvement: Continual improvement seeks to eliminate waste in all forms, improve quality of products and services, and improve customer responsiveness.
Elimination of Waste: Reducing non-value work towards the end product will result in lower manufacturing cost.
10. Discuss automation system ideas for JIT/lean.
JIT/lean and automation are mutually exclusive. Rather, it is more meaningful to discuss the processes that use humans and manual machines than the same processes powered by robots. If the fundamentals where humans apply are understood, the same fundamentals will be useful in an automated plant. All the same rules apply. We are not anti-automation.
Automation may be advantageous in many applications, but if you have not solved the problems in the human operated versions of those same applications, you are not ready to automate them effectively. If you try, you will automate your problems and will find the robots far less adept at working around them than the humans they replaced.
Social Networking Articles
Morphing membrane improves battery charge times, stops leakage
The researchers at Ohio State University are working on a “smart” membrane, which would result in faster charging batteries capable of holding their charge when not in use. Existing batteries use separators for membranes which conduct the charge while keeping anode and cathode apart. These membranes leak charge, which reduces the battery’s effectiveness over time.
The OSU researchers mimicked the function of human cell membranes which open and close tiny pores in response to electrical stimuli. The result was an electrically conductive polymer that shrinks to open the holes while the battery is in use or charging, and expands to close them when turned off. This could be of most important use in case of electric and hybrid vehicles where in the introduction of redox transistor helps to improve the charge of the vehicle with ten miles per minute of charge. The other plus point of this is that it can be either charged or it can be refilled. This research will lead to development of efficient vehicles in the automobile industry, and also it would help in solving the discharging of the batteries. The cost of these batteries wouldn’t be an issue as it can be recharged more times compared to the existing batteries.
Click here for the reference article.
SpaceX Dragon Heads Back To Earth With Station Science, Gear
SpaceX, a private space transportation company developed a free flying spacecraft designed to deliver both cargo and people to orbiting destinations. This spacecraft, named Dragon headed back to earth in late August, carrying science experiments and gear from the international space station. Astronauts aboard the space station used a big robotic arm to release the capsule 250 miles above Timor Sea north of Australia. Dragon delivered a new docking port last month that will be used in another year or two by SpaceX and Boeing, which are developing crew capsules for NASA.
SpaceX is the only firm capable of returning items for analysis back to earth. Other spaceships in the industry burn up upon re-entry into the atmosphere.
Click here for the reference article.
Click here for the detailed discussion.
Tug Boats Help Refloat Oil Rig That Ran Aground On Scottish Coast
A Transocean Winner oil rig that ran aground on a remote Scottish shore has now been towed off the rocky coast by two tug boats. The small boats towed the 19,000-ton rig “safely off the rocks”. The salvage team took advantage of high water levels, which in part helped in refloating the stranded rigs. Most of the fuel aboard the rig evaporated while it was stranded, while the rest was transferred to a supply vessel. Two of the four tanks were intact, while the other two were breached. The timely action by the crew on-board prevented huge quantity of oil from spilling into the sea.































 In the month of September, amidst a flurry of announcements about partnerships between automobile industries and tech giants, Delphi Automotive – an electronics company and Mobileye – the Israeli software maker, joined hands to develop a fully autonomous driving platform in around two years.
In the month of September, amidst a flurry of announcements about partnerships between automobile industries and tech giants, Delphi Automotive – an electronics company and Mobileye – the Israeli software maker, joined hands to develop a fully autonomous driving platform in around two years. Perlan II is the second generation glider of the Perlan Project, which was originally founded as an aviation record-setting research project by NASA. In 2006, the Perlan I achieved its first flight to greater than 50,000 feet. Immediately following that flight the team envisioned a better, pressurized aircraft that could fly higher. The Perlan II is also equipped with scientific instruments that will be used for climate, aerospace and stratospheric research that cannot be measured via other means. Among the research related goals are to measure the atmospheric concentration of aerosols and greenhouse gases, including ozone, methane and water vapor. Perlan II will also collect data on exchanges between gases and energy within the two lower layers of the Earth’s atmosphere, the troposphere and stratosphere, according to the Perlan Project website.
Perlan II is the second generation glider of the Perlan Project, which was originally founded as an aviation record-setting research project by NASA. In 2006, the Perlan I achieved its first flight to greater than 50,000 feet. Immediately following that flight the team envisioned a better, pressurized aircraft that could fly higher. The Perlan II is also equipped with scientific instruments that will be used for climate, aerospace and stratospheric research that cannot be measured via other means. Among the research related goals are to measure the atmospheric concentration of aerosols and greenhouse gases, including ozone, methane and water vapor. Perlan II will also collect data on exchanges between gases and energy within the two lower layers of the Earth’s atmosphere, the troposphere and stratosphere, according to the Perlan Project website. The U.S. Air Force and Rockwell Collins collaborated in a demonstration to transfer data from a C-17 airborne aircraft to a ground station over a Wideband High Frequency (WBHF) channel. The event took place over the duration of a two-day flight between Dover AFB Delaware and Joint Base Lewis-McChord, Washington, using a Wideband HF Receiver-Exciter configured for airborne operation.
The U.S. Air Force and Rockwell Collins collaborated in a demonstration to transfer data from a C-17 airborne aircraft to a ground station over a Wideband High Frequency (WBHF) channel. The event took place over the duration of a two-day flight between Dover AFB Delaware and Joint Base Lewis-McChord, Washington, using a Wideband HF Receiver-Exciter configured for airborne operation.










 Dyson introduced all-powerful air manipulator which incorporates the functionalities of air purifiction, heating and cooling. For purification purposes, it uses a 360-degreee HEPA filter which is capable of detecting pollutants such as pollens, molds and bacteria. The air quality parameters can be controlled via a Dyson link app, allowing users to monitor the air quality without having to walking up-to the air manipulator time and again. The funnel shape enables the air stream tto accelerate over an airfoil, thereby making the product more economical in terms of power consumption compared to a conventional fan used to maintain the air-flow over that same area. The only safety hazard I am worried about is that over the period of operation, inside surface of the funnel heats up. Making it dangerous in an environment with kids around.
Dyson introduced all-powerful air manipulator which incorporates the functionalities of air purifiction, heating and cooling. For purification purposes, it uses a 360-degreee HEPA filter which is capable of detecting pollutants such as pollens, molds and bacteria. The air quality parameters can be controlled via a Dyson link app, allowing users to monitor the air quality without having to walking up-to the air manipulator time and again. The funnel shape enables the air stream tto accelerate over an airfoil, thereby making the product more economical in terms of power consumption compared to a conventional fan used to maintain the air-flow over that same area. The only safety hazard I am worried about is that over the period of operation, inside surface of the funnel heats up. Making it dangerous in an environment with kids around.
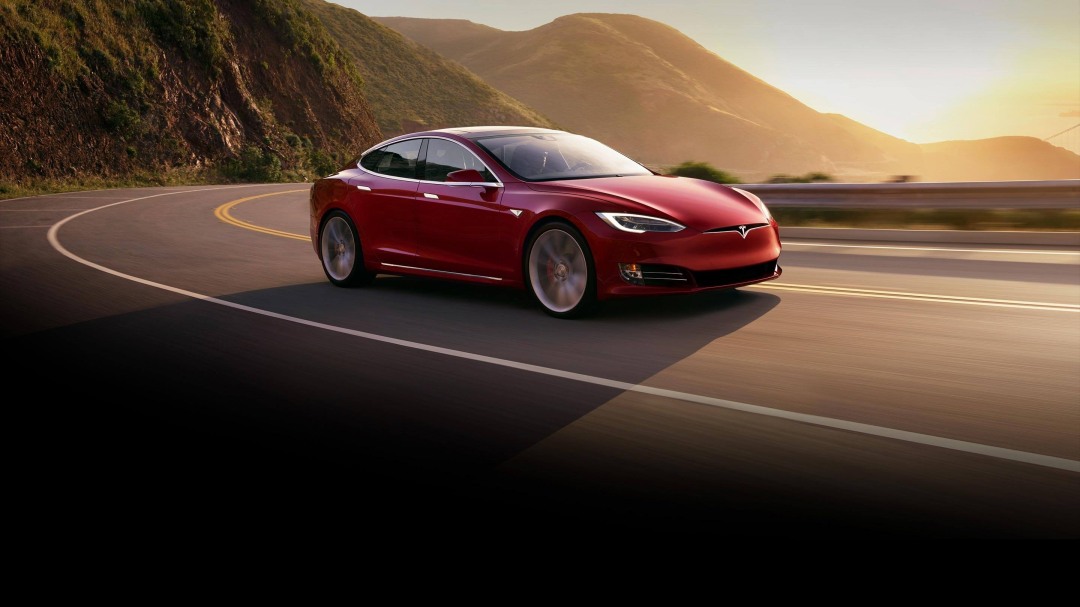
 The Model S P100D with Ludicrous mode is the third fastest accelerating production car ever produced, with a 0-60 mph time of 2.5 seconds. the article linked below talks about development and the improvements with the battery life which provides an extra 10 kWh. This feature in turn enables the car to glide 315 miles in a single charge, making it a reliable long range electric car available in today’s automobile market.
The Model S P100D with Ludicrous mode is the third fastest accelerating production car ever produced, with a 0-60 mph time of 2.5 seconds. the article linked below talks about development and the improvements with the battery life which provides an extra 10 kWh. This feature in turn enables the car to glide 315 miles in a single charge, making it a reliable long range electric car available in today’s automobile market.
